
Electrical and Electronics Engineering (EEE) is a field that combines power systems, electronics, and control systems. Working on practical projects helps students understand theoretical concepts better and prepares them for real-world challenges. These projects range from simple circuits for beginners to complex systems for final-year students. Whether you want to learn basic electronics or build advanced automation systems, hands-on projects are the best way to develop your skills and boost your confidence. In this blog, we have given the top 15 project ideas for EEE engineering students based on the levels of difficulty – beginner, intermediate and advanced.
In Mahalakshmi Tech Campus, our expert faculties guides the students to choose the right kind of project and helps all along to build the chosen project in an effective manner!
15 Project Ideas for EEE Students by Difficulty Level
In the following table, we have classified the projects for EEE engineering students based on their difficulty level. It will be convenient for the EEE students to go through and pick the one.
S.No | Beginner | Intermediate | Final Year/Advanced |
1 | Automatic Street Light | Home Automation System | Smart Grid Management System |
2 | Clap Switch | Solar Panel Tracking System | Electric Vehicle Charging Station |
3 | Water Level Indicator | Automatic Plant Watering System | Wireless Power Transfer System |
4 | Touch Dimmer Switch | RFID-Based Attendance System | Fault Detection in Power Lines |
5 | Simple Burglar Alarm | Temperature-Based Fan Speed Controller | Industrial Motor Protection System |
1. Automatic Street Light

Description: An automatic street light is a simple circuit that turns lights on when it gets dark and off when there is enough sunlight. It uses a Light Dependent Resistor (LDR) to sense light levels. When darkness falls, the LDR resistance increases, which triggers a relay to switch on the light. This project for EEE engineering students saves energy by ensuring lights only work when needed.
Benefits:
- Learn about basic sensors and how they work
- Understand relay operation and switching circuits
- Develop energy-saving solutions
- Simple circuit that shows real-world applications
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic understanding of resistors and transistors
- Knowledge of how LDR sensors work
- Ability to read simple circuit diagrams
- Basic soldering skills
Required Tools and Processes:
- LDR sensor
- Relay module
- Transistor (BC547 or similar)
- Resistors and connecting wires
- LED or bulb for output
- Breadboard for testing
- Soldering iron for final circuit
- Multimeter for testing connections
2. Clap Switch
Description: A clap switch controls electrical devices by detecting sound. It uses a small microphone to pick up clapping sounds. When you clap, the circuit processes the sound signal and toggles a relay to turn devices on or off. This EEE engineering project demonstrates sound sensing and basic signal processing in a fun way.
Benefits:
- Learn about sound sensors and audio signal detection
- Understand basic digital logic and flip-flop circuits
- Create a practical device for hands-free control
- Improve circuit design skills
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic electronics and component identification
- Understanding of operational amplifiers
- Knowledge of digital logic gates
- Simple circuit assembly skills
Required Tools and Processes:
- Condenser microphone
- Operational amplifier (IC 741)
- Flip-flop IC (CD4017 or 555 timer)
- Relay and transistor
- Resistors and capacitors
- Battery or power supply
- Breadboard and connecting wires
- Soldering equipment
3. Water Level Indicator
Description: A water level indicator shows how much water is in a tank using LED lights. It uses probes placed at different heights inside the tank. When water touches a probe, it completes a circuit and lights up the corresponding LED. This helps people know when to refill or stop filling the tank.
Benefits:
- Learn about conductivity and water as a conductor
- Understand simple sensing mechanisms
- Build a useful device for homes and industries
- Practice basic circuit connections
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic understanding of electrical conductivity
- Knowledge of transistor working as a switch
- Ability to work with simple circuits
- Understanding of LED operation
Required Tools and Processes:
- Transistors (BC547)
- LEDs of different colors
- Resistors
- Copper wires or metal probes
- Container for testing
- Breadboard
- Power supply (9V battery)
- Connecting wires
4. Touch Dimmer Switch

Description: A touch dimmer switch changes the brightness of a light by simply touching a metal plate. It uses your body’s capacitance to detect touch and adjusts light intensity accordingly. Each touch increases or decreases brightness in steps, giving you full control without traditional switches.
Benefits:
- Learn about touch sensing technology
- Understand PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) for dimming
- Create modern switch alternatives
- Develop skills in AC circuit control
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic understanding of capacitive sensing
- Knowledge of TRIAC for AC control
- Understanding of PWM technique
- Circuit testing and debugging skills
Required Tools and Processes:
- Touch sensor module or IC (like 555 timer)
- TRIAC (BT136)
- Resistors and capacitors
- Metal touch plate
- LED or incandescent bulb
- PCB or breadboard
- Soldering tools
- Oscilloscope for testing (optional)
5. Simple Burglar Alarm
Description: A simple burglar alarm detects intruders using basic sensors like IR sensors or magnetic switches. When someone breaks the sensor beam or opens a door, the circuit triggers an alarm buzzer or siren. This project for EEE engineering students teaches security system basics and sensor integration.
Benefits:
- Learn about security system fundamentals
- Understand different types of sensors
- Build a practical home security device
- Develop troubleshooting skills
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic circuit design knowledge
- Understanding of IR sensors or magnetic switches
- Knowledge of alarm circuit operation
- Simple programming (if using microcontroller)
Required Tools and Processes:
- IR transmitter and receiver OR magnetic switch
- Buzzer or siren
- Transistor or relay
- Resistors
- Power supply
- Breadboard and wires
- Enclosure for mounting
- Testing equipment
6. Home Automation System

Description: A home automation system lets you control home appliances like lights, fans, and other devices using your smartphone or voice commands. It uses a microcontroller connected to the internet through WiFi. You can turn devices on or off remotely through a mobile app, making your home smarter and more convenient.
Benefits:
- Learn about IoT (Internet of Things) technology
- Understand wireless communication protocols
- Build practical smart home solutions
- Develop mobile app integration skills
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Microcontroller programming (Arduino or NodeMCU)
- Basic understanding of WiFi modules
- Knowledge of relay control circuits
- Mobile app basics (Blynk or similar platforms)
Required Tools and Processes:
- NodeMCU or ESP8266 WiFi module
- Relay modules (4-channel or 8-channel)
- Resistors and connecting wires
- Home appliances for testing
- Arduino IDE software
- Smartphone with Blynk or similar app
- Power supply (5V adapter)
- Breadboard for prototyping
7. Solar Panel Tracking System
![]()
Description: A solar panel tracking system automatically moves solar panels to follow the sun throughout the day. It uses light sensors (LDRs) to detect the sun’s position and servo motors to adjust the panel angle. This increases solar energy collection by 30-40% compared to fixed panels.
Benefits:
- Learn about renewable energy optimization
- Understand servo motor control
- Work with sensor feedback systems
- Build an environmentally friendly project
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Microcontroller programming (Arduino)
- Understanding of servo motor operation
- Knowledge of LDR sensor arrays
- Basic mechanical assembly skills
Required Tools and Processes:
- Arduino board (Uno or Nano)
- Two servo motors
- Four LDR sensors
- Small solar panel
- Resistors and potentiometers
- Mounting frame (wood or metal)
- Connecting wires
- Power supply
- Arduino IDE software
8. Automatic Plant Watering System
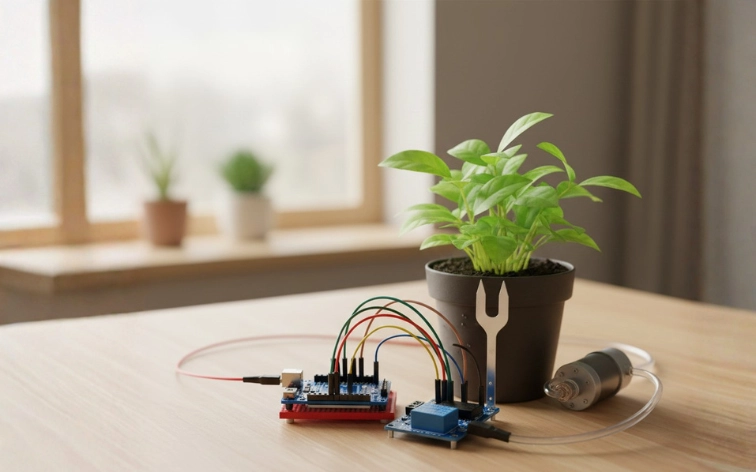

Description: An automatic plant watering system waters plants when the soil becomes dry. It uses a soil moisture sensor to check moisture levels. When the soil is dry, the system turns on a water pump for a specific time. This ensures plants get the right amount of water without manual monitoring.
Benefits:
- Learn about agricultural automation
- Understand moisture sensing technology
- Build a practical gardening solution
- Develop timer-based control systems
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Basic microcontroller programming
- Understanding of soil moisture sensors
- Knowledge of motor driver circuits
- Timing and control logic
Required Tools and Processes:
- Arduino or similar microcontroller
- Soil moisture sensor
- Water pump (12V DC)
- Motor driver module (L293D)
- Relay module
- Plastic tubing
- Resistors and wires
- Power supply (12V)
- Container for water reservoir
9. RFID-Based Attendance System
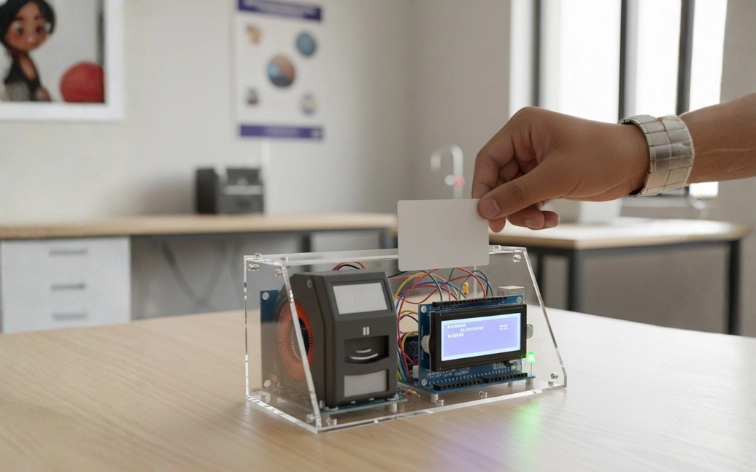

Description: An RFID-based attendance system records student or employee attendance automatically. Each person has an RFID card or tag. When they tap the card on the reader, their attendance is recorded with a timestamp. The data can be stored on an SD card or sent to a computer for record-keeping.
Benefits:
- Learn about RFID technology and wireless identification
- Understand data logging systems
- Build automated attendance solutions
- Work with display and storage modules
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Microcontroller programming (Arduino)
- Understanding of RFID communication protocol
- Knowledge of LCD display interfacing
- Basic data storage concepts
Required Tools and Processes:
- Arduino board
- RFID reader module (RC522)
- RFID cards or tags
- LCD display (16×2)
- SD card module (optional)
- Buzzer for feedback
- RTC (Real Time Clock) module
- Connecting wires
- Power supply
10. Temperature-Based Fan Speed Controller
Description: This system automatically adjusts fan speed based on room temperature. A temperature sensor continuously monitors the environment. As temperature increases, the fan speed increases proportionally. When it cools down, the fan slows down or stops. This provides comfort while saving energy.
Benefits:
- Learn about temperature sensing and control
- Understand PWM for speed control
- Build energy-efficient climate control
- Develop feedback control systems
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Microcontroller programming
- Understanding of temperature sensors (LM35 or DHT11)
- Knowledge of PWM technique
- Motor control circuit design
Required Tools and Processes:
- Arduino board
- Temperature sensor (LM35 or DHT11)
- DC fan (12V)
- Motor driver (L293D or MOSFET)
- LCD display (optional)
- Resistors and connecting wires
- Power supply (12V)
- Breadboard
- Arduino IDE
11. Smart Grid Management System
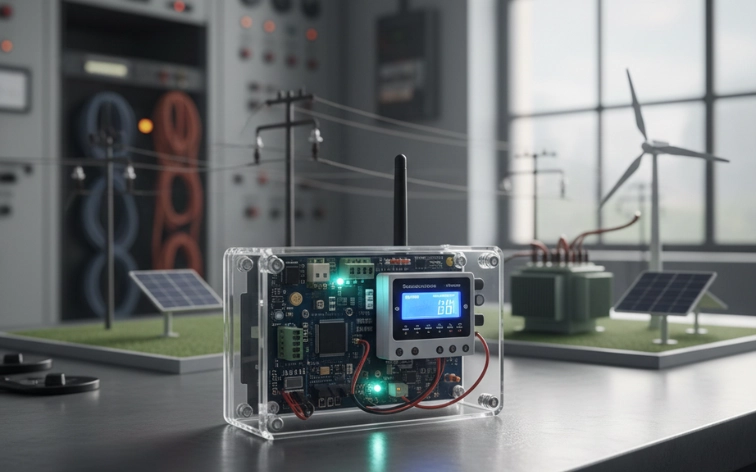
Description: A smart grid management system monitors and controls power distribution in an electrical network. It uses sensors to track voltage, current, and power consumption in real-time. The system can detect faults, balance loads, and optimize energy distribution automatically. It often includes communication modules to send data to central monitoring stations.
Benefits:
- Learn about modern power system management
- Understand industrial automation and SCADA systems
- Work with multiple sensors and complex control logic
- Develop skills in power electronics and communication
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Advanced microcontroller or PLC programming
- Understanding of power system fundamentals
- Knowledge of current and voltage sensors
- Communication protocols (Modbus, MQTT)
- Data analysis and visualization
Required Tools and Processes:
- Microcontroller (Arduino Mega) or PLC
- Voltage and current sensors (ZMPT101B, ACS712)
- GSM/WiFi module for communication
- Relay boards for control
- LCD or web dashboard for monitoring
- Power supply units
- Circuit breakers and protection devices
- Data logging system
- Computer with monitoring software
12. Electric Vehicle Charging Station
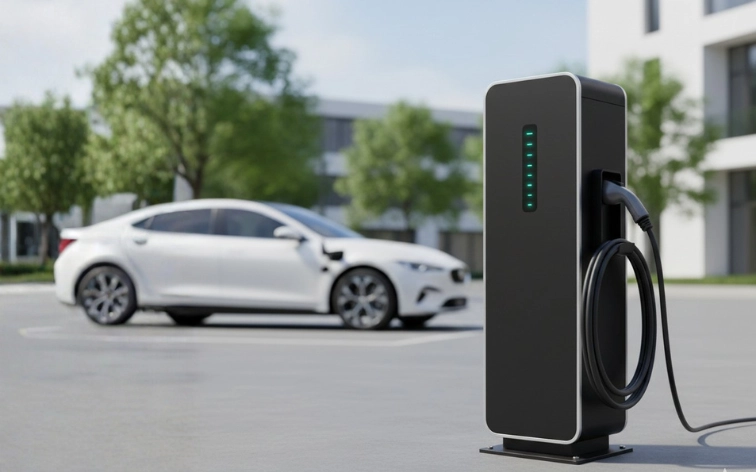

Description: An electric vehicle charging station project in EEE involves designing a system that safely charges EV batteries. It includes power conversion circuits that change AC power to DC, charging control systems that monitor battery status, and safety features like overcharge protection. The system can display charging status and calculate energy consumption.
Benefits:
- Learn about EV technology and future transportation
- Understand high-power electronics and conversion
- Work with battery management systems
- Develop commercial-grade product design skills
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Power electronics and AC-DC conversion
- Battery charging principles and protocols
- High voltage safety procedures
- Microcontroller programming for monitoring
- Display and user interface design
Required Tools and Processes:
- Step-down transformer or SMPS
- Rectifier bridge and filter capacitors
- Buck converter for DC-DC conversion
- Microcontroller for control (Arduino Mega/STM32)
- Current and voltage sensing modules
- LCD touchscreen display
- Cooling system (fans or heat sinks)
- Safety relays and circuit breakers
- Proper testing equipment (oscilloscope, multimeter)
- Battery for testing
13. Wireless Power Transfer System
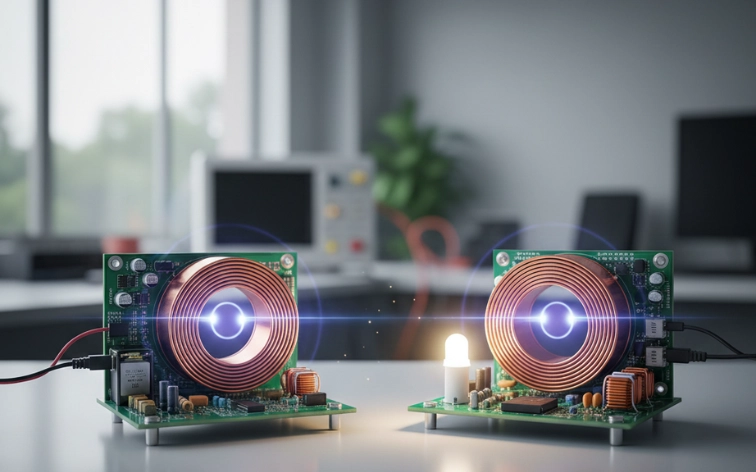
Description: A wireless power transfer system transmits electrical energy without physical wires using electromagnetic induction. It consists of a transmitter coil that creates a magnetic field and a receiver coil that captures energy from this field. This technology is used in wireless phone chargers and has potential for larger applications.
Benefits:
- Learn about electromagnetic induction principles
- Understand resonant circuits and frequency tuning
- Work with high-frequency electronics
- Explore cutting-edge wireless technology
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Advanced understanding of electromagnetic theory
- Knowledge of resonant circuit design
- High-frequency circuit design skills
- Safety awareness for RF systems
- Coil design and optimization
Required Tools and Processes:
- Signal generator or oscillator circuit
- Power amplifier (MOSFET-based)
- Transmitter coil (self-wound or purchased)
- Receiver coil (matched to transmitter)
- Resonant capacitors
- Rectifier and voltage regulator
- Load for testing (LED or small device)
- Oscilloscope for frequency checking
- Power supply
- Safety equipment
14. Fault Detection in Power Lines
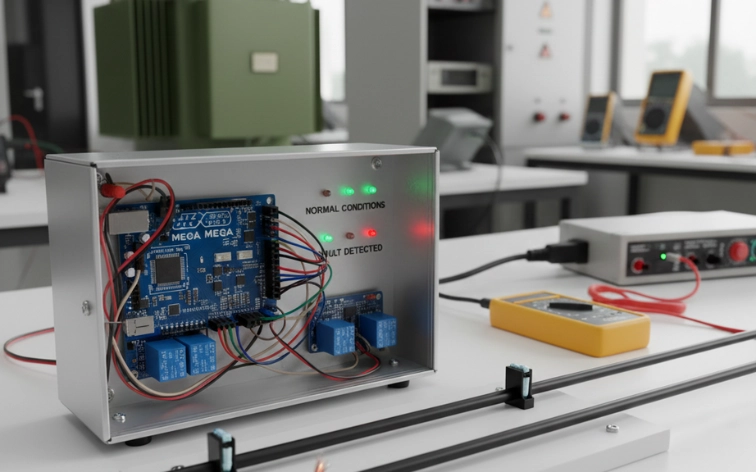
Description: This system detects and locates faults in electrical transmission lines using microcontroller-based monitoring. It continuously measures voltage and current at different points. When a fault like short circuit or line break occurs, the system identifies the fault type and calculates its distance from the monitoring point using impedance calculations.
Benefits:
- Learn about power system protection
- Understand fault analysis techniques
- Work with real-world utility problems
- Develop complex algorithm implementation skills
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Power system analysis and fault calculations
- Advanced microcontroller programming
- Signal processing and filtering
- Communication system integration
- Understanding of transmission line theory
Required Tools and Processes:
- Microcontroller (Arduino Mega or STM32)
- Precision voltage sensors
- Current sensors (high accuracy)
- GPS module for location tracking
- GSM module for alert transmission
- LCD display for local monitoring
- Miniature transmission line model for testing
- Data acquisition system
- Protection relays
- Computer for data analysis
15. Industrial Motor Protection System
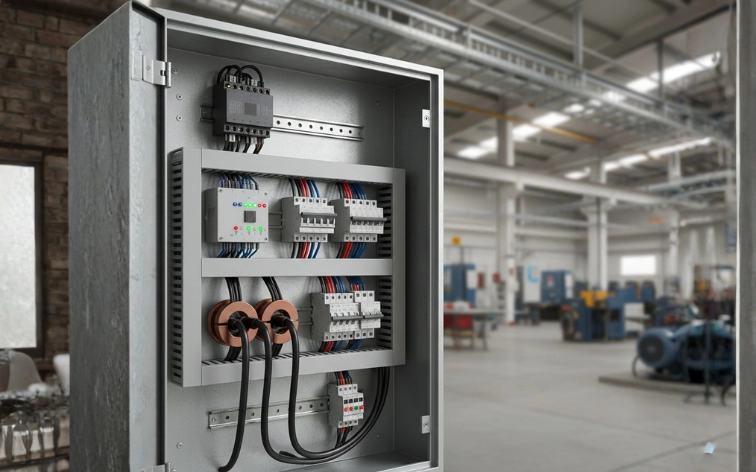

Description: An industrial motor protection system safeguards three-phase motors from various electrical faults. It monitors parameters like overcurrent, undervoltage, overvoltage, phase failure, and overheating. When any abnormal condition is detected, the system trips the motor and sends alerts. It includes automatic restart features and maintains fault logs for analysis.
Benefits:
- Learn about industrial automation and protection
- Understand three-phase power systems
- Work with multiple protection algorithms
- Develop skills valuable for industrial employment
Required Knowledge and Skills:
- Three-phase motor working principles
- Advanced microcontroller programming
- Understanding of various electrical faults
- Current and voltage measurement techniques
- PLC programming (optional but beneficial)
Required Tools and Processes:
- Microcontroller or PLC
- Three-phase voltage sensors
- Current transformers for each phase
- Temperature sensor (thermocouple or RTD)
- Relay board for motor control
- Contactor for switching
- LCD display with keypad
- Buzzer and indicator LEDs
- Data logging system (SD card or cloud)
- Small three-phase motor for testing
- Proper safety equipment and isolation
Also read: EEE engineering scope
Mini Projects for EEE Students at Low Cost
Below, we have given several mini projects for EEE students that can be done at an affordable cost. It can be used by the EEE engineering students at any difficulty levels – beginner, intermediate and advanced/final year:
- Automatic Room Light Controller Using PIR Sensor: Uses motion detection to turn lights on when someone enters and off when the room is empty
- Mobile Phone Detector Circuit: Detects active mobile phones in restricted areas by sensing RF signals during calls or data transmission
- Electrical Appliance Control Using TV Remote: Reuses old TV remotes to control home appliances through infrared communication
- Automatic Railway Gate Controller: Operates railway crossing gates automatically when a train approaches using IR sensors
- Dark Activated Switch Using Transistor – Simple circuit that activates any device automatically when ambient light falls below a set level
- Coin-Based Mobile Charging System – Public charging station that activates for a fixed time when a coin is inserted, useful for railway stations and bus stands
- Fire Alarm System Using Temperature Sensor: Detects sudden temperature rise and triggers alarm to alert about potential fire hazards
- Electronic Code Lock: Digital security lock using basic keypad and logic gates, without expensive microcontrollers
- Visitor Counter Using IR Sensors: Counts people entering and exiting a room, useful for monitoring capacity in shops and classrooms
- Automatic Battery Charger With Overcharge Protection: Charges batteries automatically and cuts off power when fully charged to prevent damage
Conclusion
Working on practical projects is essential for EEE engineering students to bridge the gap between theory and real-world applications. Starting with simple projects like automatic street lights and gradually moving to advanced systems like smart grids helps you build confidence and skills step by step. Each project idea for EEE engineering students teaches valuable lessons about circuits, programming, problem-solving, and system design. Whether you choose beginner or advanced projects, remember that hands-on experience is the best teacher. These projects not only improve your technical knowledge but also make you more attractive to employers. Start with projects that match your current skill level, learn from mistakes, and gradually take on more challenging work. The skills you develop through these projects will serve you throughout your engineering career.
Related Blogs
- Mini Project Ideas for CSE Students
- Top Final Year Project Ideas for CSE Students
- Mini Project Ideas for ECE Students
- Best AI Project Ideas for Students
- Top Cybersecurity Projects for Students
FAQs
1. What is the best project for EEE engineering student with no experience?
The best starting project is an automatic street light or water level indicator. These projects use simple components like LDR sensors and transistors, require minimal programming, and teach fundamental concepts. They are affordable, easy to troubleshoot, and can be completed in a few days with basic tools.
2. Which microcontroller is best for EEE projects?
Arduino is the best choice for beginners due to its simple programming language, large community support, and extensive documentation. For advanced projects, STM32 or ESP32 offer more power and features. Raspberry Pi is ideal when you need a computer-like environment with Linux support.
3. Do I need programming knowledge for EEE projects?
Basic projects can be done without programming using simple circuits. However, intermediate and advanced projects require programming skills. Learning Arduino programming (similar to C++) is recommended as it’s easy to understand and widely used in electronics projects.
4. What are the most important skills for completing EEE projects?
The key skills include circuit design, component identification, soldering, basic programming, troubleshooting with multimeters, reading datasheets, and understanding electrical safety. Problem-solving and patience are equally important when debugging circuits that don’t work initially.
5. Can EEE projects help in getting job placements?
Yes, completing quality projects significantly improves placement chances. Projects demonstrate practical skills, problem-solving ability, and initiative to employers. Having 2-3 well-documented projects in your portfolio shows you can apply theoretical knowledge to real problems.
6. What is the difference between EEE and ECE projects?
EEE projects focus more on power systems, electrical machines, power electronics, and control systems. ECE projects emphasize communication systems, signal processing, embedded systems, and VLSI. However, in EEE vs ECE, there is considerable overlap in microcontroller-based projects.
7. How long does it take to complete an EEE final year project?
Final year projects typically take 3-6 months to complete properly. This includes literature review, design, component procurement, implementation, testing, documentation, and presentation preparation. Starting early and working consistently gives the best results.
8. Where can I buy components for my EEE project?
You can buy components from online stores like Amazon, electronic component websites, or local electronics markets. Popular online retailers include DigiKey, Mouser, and SparkFun internationally, or local suppliers in your country. Compare prices and check reviews before purchasing.
9. What safety precautions should I take during EEE projects?
Always work with proper voltage ratings, use insulated tools, never touch live circuits, keep water away from electrical components, use fuses and circuit breakers, work in well-ventilated areas (especially when soldering), and understand the circuit before powering it up. For high-voltage projects, work under supervision.
10. How do I choose a final year project topic?
Choose a topic based on your interests (power systems, renewable energy, automation, etc.), future career goals, available resources, and current industry trends. Discuss with faculty advisors, research recent publications, and ensure the project is challenging but achievable within your timeframe.




